Diverting Acid Technology Overview
For heterogeneous reservoirs, conventional acid systems tend to preferentially penetrate some large pores or high-permeability parts of the reservoir, and the acid has difficulty reaching the low-permeability parts of the reservoir, which are the parts that need to be enhanced. When conventional hydrochloric acid is used to acidize carbonate formations, some main channels are formed in the bedrock by acid dissolution, and the acid flows along these channels, without acidizing other rocks. At this point, if a diverting agent is added to the conventional acid, the diverting agent will temporarily plug these channels, change the acid injection flow direction, and make the acid enter the relatively low-permeability area and react with the unacidized reservoir part. That is, by temporarily plugging the large pores or high-permeability zones of the reservoir,forcing the acid to divert to the low-permeability zones, to achieve simultaneous improvement of the high-permeability and low-permeability zones of the reservoir, this is diverting acid technology.
After being injected into the formation at high pressure, diverting acid will first follow larger pores enter reservoirs with higher permeability, and react with carbonate rocks. Due to the reaction, the pH value of the acid increases and Ca+ ions are produced. The surfactant in VES diverting acid is usually a gemini quaternary ammonium salt surfactant, which has the feature that when the pH value, the Ca+ ion concentration and the viscosity are very low (close to water viscosity), as the acid-rock reaction progresses, The pH value keeps rising, and the viscosity of the acid gradually increases. When the pH value reaches 2.0-4.0, the viscosity of the acid sharply increases and forms a high-viscosity gel distributed on the surface of pores, cracks, and holes, reducing liquid loss. At the same time, it makes fresh acid continue to penetrate deeper and divert to other low-permeability layers, thereby increasing the effective action distance of the acid.
After the acid reaches the target layer, this high-viscosity gel will contact oil, gas or formation water. At this point, the gel bundle is destroyed and changes from rod-shaped to spherical. The viscosity of the acid decreases because the gel bundle no longer entangles. The viscosity drops from hundreds of centipoises to about 10mPa.s of original thickening base fluid viscosity. The system completely breaks down. This makes it easy for liquid entering the formation to be discharged from the formation.
1、Liquid preparation
We have an excellent service team that will arrive at the site as soon as they get the production task.
2、Operation block
(1)Moxi 121 well: It is an evaluation well located in the Moxi 52 well area in the northern section of the Moxi platform edge belt of the Leshan-Longnvsi uplift in Sichuan Basin. This well was improved using diverting acid technology. The acidizing additives were provided by our company. The drilling depth was 5579m and drilled through the Deng 4 section with open hole completion. This time 5432.0~5579.0m was acidized. Because this layer has a long open hole section and strong reservoir heterogeneity, in order to enhance the construction effect of the whole well section, low-friction, temperature-resistant and good diverting performance diverting acid was used to achieve uniform placement of long well section acid and improve whole well efficiency; construction time was from February 9th to February 11th in 2018; operation liquid totalled 154m3 as shown in the table below:
|
Fluid Used
|
Volume/m³
|
Formula
|
|
Diverting Acid
|
120
|
20%HC1+5% Diverting Acid Diverting Agent+2% Diverting Acid Corrosion Inhibitor+1%Acidizing Iron Ion Stabilizer
|
|
Friction-reducing Fluid
|
24
|
1% Friction-reducing Agent+1%Drainage Aid
|
|
Post-flush Fluid
|
10
|
1% Clay Stabilizer+1% Drainage Aid+10% Diverting Acid Mutual Solvent
|
Liquid preparation construction was tracked by our company’s personnel on well throughout the process; diverting acid was 20m³/barrel with a total of 6 barrels; liquid preparation concentration was 20±1%; fresh acid viscosity was 5±0.5 (170s-1、mPa·s); test results met construction design requirements.
|
Parameter
|
Pump Pressure
|
Displacement
|
Balance Pressure
|
|
Unit
|
MPa
|
m3/min
|
MPa
|
|
Highest
|
94
|
3.5
|
35
|
|
Lowest
|
40
|
1.2
|
12
|
|
Average
|
86-93
|
3.3-3.5
|
30-35
|
|
Fracturing truck
|
2000 type fracturing truck 7 units
|
Operation time
|
72min
|
High pressure time
|
61min
|
Operation Curve:
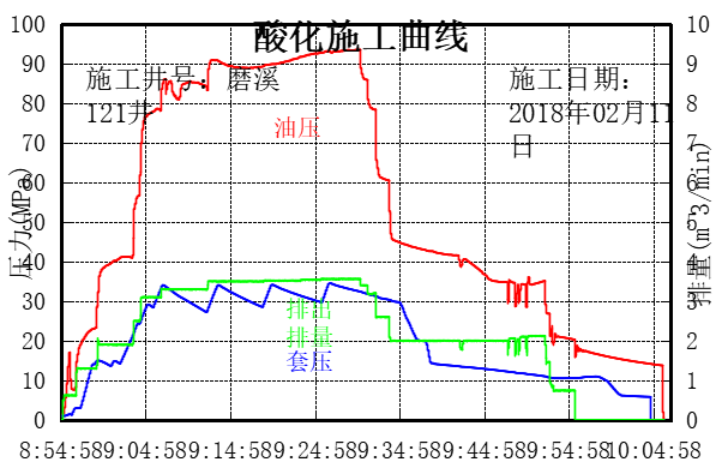
We tested our acidizing modification fluid and confirmed that it met our design standards. We used 154m3 of fluid for both design and operation and injected it into the well at a rate of 3.3~3.5 m³/min and a pressure of 86-93MPa. The operation took 72 minutes and was completed successfully;
After acidizing, we discharged 136.2m3 of liquid and achieved a steady and high output of 341,500m³/day.
(2)Shengtan 1 well: we started our fluid operation on December 11, 2022, using 520 m³ of diversion acid
After acidizing, we closed the well for 2 hours to discharge the liquid. We recorded a discharge volume of 129m³, an oil pressure of 20.5 MPa, a casing pressure of zero MPa, a flame height of 5-7 meters, and an initial production rate of 280,000m³/day.









